How Do Conditions in the Ocean Change With Depth
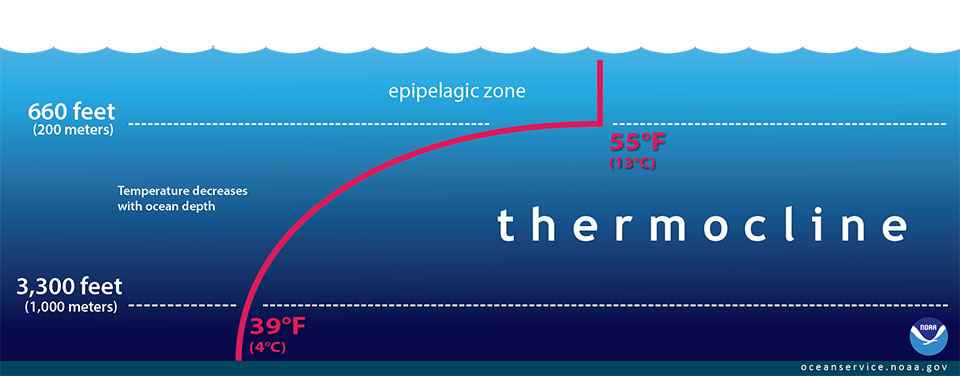
The red line in this illustration shows a typical seawater temperature profile. The water molecules pack together tighter as pressure increases the pressure increase with depth due to the weight of the water above and causes the greatest density changes in seawater with depth greater than the density.

2351 Photography By Peter Holme Iii Bit Ly 14jr70n Rock Surfer Wave Sports Surfing Waves Surfing Photography Surfing
Your email address will not be published.

. Temperature decreases and pressure decreases. A new study from MIT researchers published last month in Nature Communications provides evidence that not only do certain currents become stronger in certain seasons but also that this seasonality affects both marine life and climate. How do conditions change as the depth of the ocean water increases.
Required fields are marked Comment. Temperature increases and pressure decreases. How do conditions change as the depth of the ocean water increases.
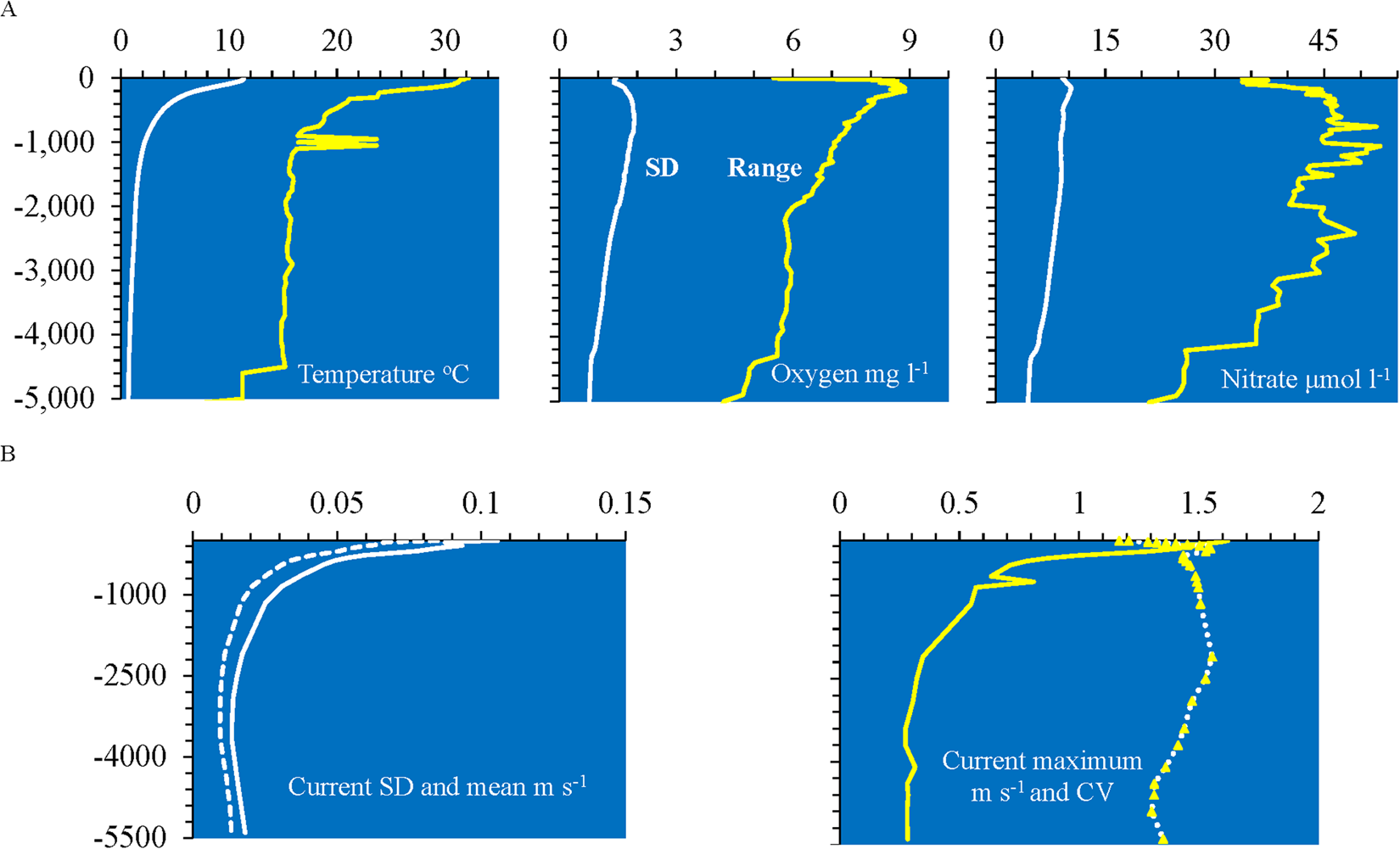
Below that the temperature stays at about 35 C throughout most of the ocean. Oceanographers make these graphs because many of the properties of seawater change with depth. How Do Conditions In The Ocean Change With Depth.
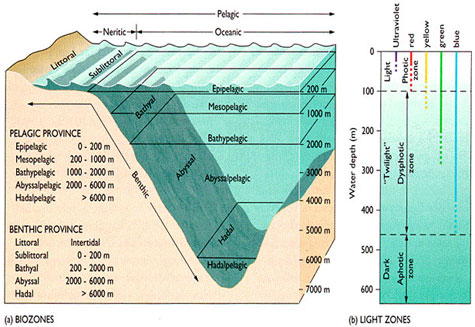
In the thermocline temperature decreases rapidly from the mixed upper layer of the ocean called the epipelagic zone to much colder deep water in the thermocline mesopelagic zone. How do conditions change as the depth of the ocean water increases. The ocean and atmosphere are inextricably.
Use the information for informational purposes only. Cold water is also more dense and as. Temperature is one property that does just this.
41100000 surface area sq mi 28681 max. Temperature decreases and pressure increases. In the ocean solar energy is reflected in the upper surface or rapidly absorbed with depth meaning that the deeper into the ocean you descend the less sunlight there is.
The water in Earth oceans varies in salinity temperature and depth. Up to 24 cash back would pass through a vertical section of the ocean called the water column. The salinity in Earths oceans changes because of different events occurring in the Water Cycle.
This is due to an increase in hydrostatic pressure the force per unit area exerted by a liquid on an object. Without the ocean Earth would be much hotter than it is right now. As you travel from the surface of the ocean downward to the seafloor water pressure increases by one atmosphere or 14 pounds per square inch for every 10 meters 328 feet of depth.
Below 3300 feet to a depth of about 13100 feet water temperature remains constantAt depths below 13100 feet. The conditions in the deep ocean are vastly different and arguably more extreme than those found in more shallow ocean waters making these habitats different from other places on Earth. In the ocean solar energy is reflected in the upper surface or rapidly absorbed with depth meaning that the deeper into the ocean you descend the less sunlight there is.
When water evaporates salinity is greater because the salt is left behind when the water evaporates. Sunlight is quickly absorbed in the upper layers of water resulting in higher temperatures there than in deeper water. Conditions change greatly as you travel down through the water column.
The deeper you go under the sea the greater the pressure of the water pushing down on you. How do conditions change as the depth of the ocean water increases. Even if you live on land like humans do you wouldnt survive without the ocean.
The depth map shows marine chart of Atlantic Ocean. How do the ocean conditions change as the depth of the water increases. Temperature often decreases as depth increases since the source of the heat is the sun.
This results in less warming of the water. Little or no light penetrates this part of the ocean and most of the organisms that live there rely for subsistence on falling organic matter produced in the photic zoneFor this reason scientists once assumed that life would be. The ocean is a home and food source for countless fish mammals plants birds and more.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply. It drops to about 4C at 1 kilometer below the surface. The ocean plays an important role in whatever happens in our environment on Earth.
Explain how salinity changes in Earths oceans. For every 33 feet 1006 meters you go down the pressure increases by one atmosphere. As the ocean gets deeper light temperature and dissolved oxygen decrease while pressure and nutrients increase.
Name Email. Depth ft Nearby waterbodies 445 Absecon Bay NJ Alexander Lake CT Almy Pond. Temperature increases and pressure increases.
The deep sea or deep layer is the lowest layer in the ocean existing below the thermocline and above the seabed at a depth of 1000 fathoms 1800 m or more. As the seasons change so too does the strength of ocean currents. Below the surface zone salinity remains fairly constant throughout the water column.
Pressure increases continuously with. Rainfall decreases salinity near the surface while evaporation increases salinity in the warm dry areas. Temperature decreases and pressure increases.
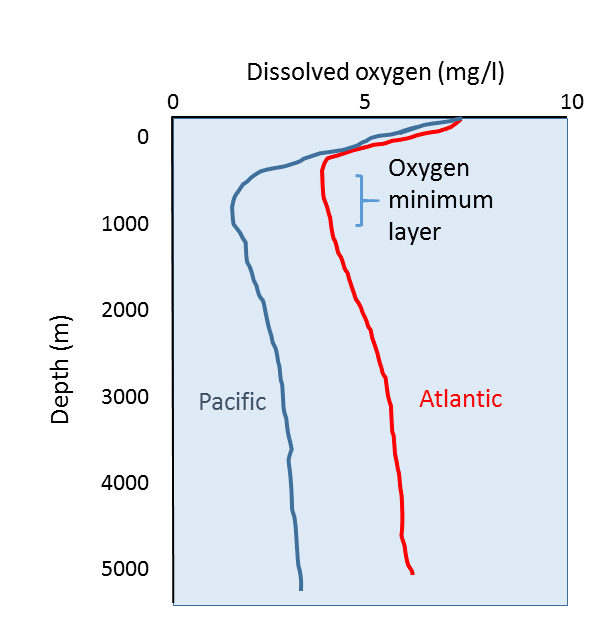
Therefore the deep ocean below about 200 meters depth is cold with an average temperature of only 4C 39F. The temperature of ocean water also varies with depth. As wer gets deeper there is less oxygen and it gets colder.
Temperature decreases as you descend through the ocean. Organisms that inhabit the various. Atlantic Ocean marine chart.
N the deep zone water is always extremely cold.

Oceanic Pressure Ck 12 Foundation
Deep Sea Biology Dive Discover

Biologists Ignore Ocean Weather At Their Peril Ocean Oceans Of The World Physical Condition

Nws Jetstream Layers Of The Ocean

Sea Or Ocean Water Surface And Underwater Split By Waterline Sea Or Ocean Water Aff Water Ocean Sea Surface Waterl Sea And Ocean Ocean Underwater

Top 10 Oceanography Books Oceanography Black History Books Books
Stratifying Ocean Sampling Globally And With Depth To Account For Environmental Variability Scientific Reports

High Pressure In The Deep Ocean Science Friday Ocean Science Science Friday Cool Science Experiments

Weather Amp Climate Precipitation Education Weather And Climate Global Weather Weather Photos

Voyage 10 Design A Critter Dissolved Oxygen Photosynthesis Oxygen

Ocean Layers Mixing Time Scavengers

The Effect Of Climate Change Across Ocean Regions Climate Change Effects Climate Change Ocean Systems
5 4 Dissolved Gases Oxygen Introduction To Oceanography

Students Investigate Conditions In The Deepest Parts Of The Ocean Make Inferences About Ocean Creatures Based On Th Underwater World Ocean Pictures Ocean Life

Chapter 16 The Ocean Depths Life In The Mesopelagic And Deep Sea Is Linked To Plankton And Light Intensity In The Water Ppt Download

No Matter What The Surface Conditions Are Stormy Or Smooth Deep In The Ocean It S Always Tranquil And Serene From The Life Quotes Time Quotes Mindfulness


Comments
Post a Comment